Conditions
Palpebral Lesions
Palpebral lesions are a common condition, and while some can be cancerous (malignant), most lesions are deemed benign (non-cancerous).
However, you should get them checked out by an ophthalmologist to make sure they’re not cancerous or pre-cancerous.
What are palpebral lesions?
Palpebral or eyelid lesions are bumps or growths on your eyelid that range from harmless lumps to severe tumours.
There are two types of eyelid lesions: benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous).
While most eyelid lesions are not life-threatening and do not lead to vision loss, your ophthalmologist should perform a comprehensive eye exam to confirm they are not cancerous or pre-cancerous growths.
In studies, around 80 to 85% of eyelid lesions that required biopsy were benign.
In one study of 408 patients, the most common eyelid lesions in order of frequency were:
- Chalazion
- Squamous papilloma
- Epidermal inclusion cyst
- Seborrheic keratosis
- Xanthelasma
- Cysts of Moll and Zeiss
- Nevus
- Verruca vulgaris
- Dermoid/epidermoid cyst
- Capillary hemangioma
- Keratoacanthoma
- Cutaneous horn
- Xanthogranuloma
- Trichoepithelioma
- Apocrine hidrocystoma
In another large study of 2639 eyelid lesions, the most common benign eyelid lesions were:
- Inflammatory (chalazion)
- Melanocytic nevus
- Squamous papilloma
- Dermoid cyst
- Epidermal inclusion cyst
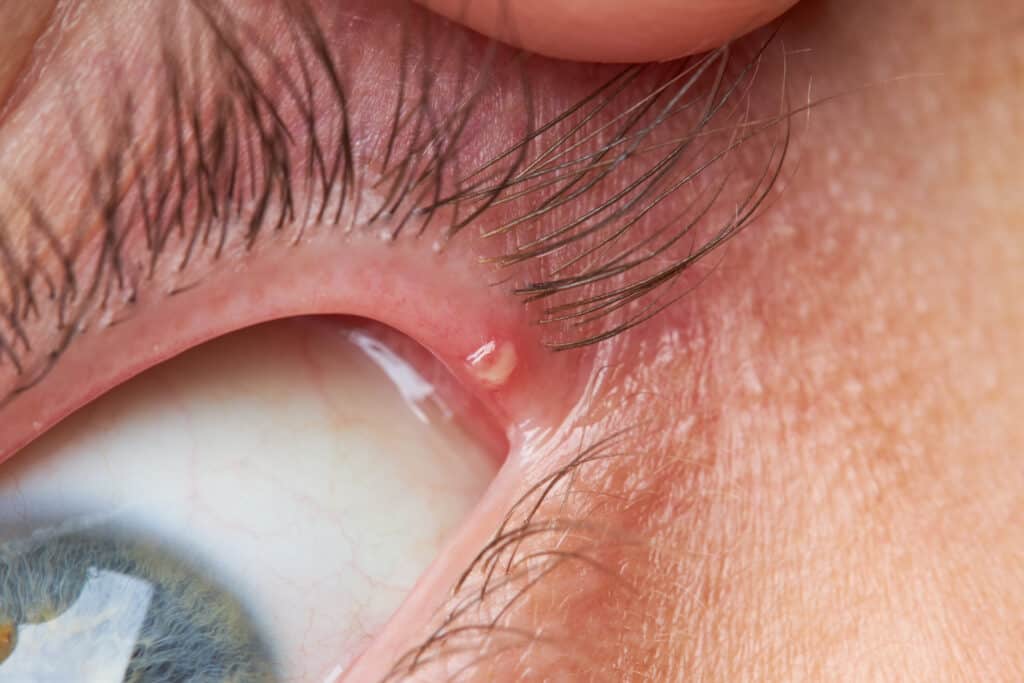
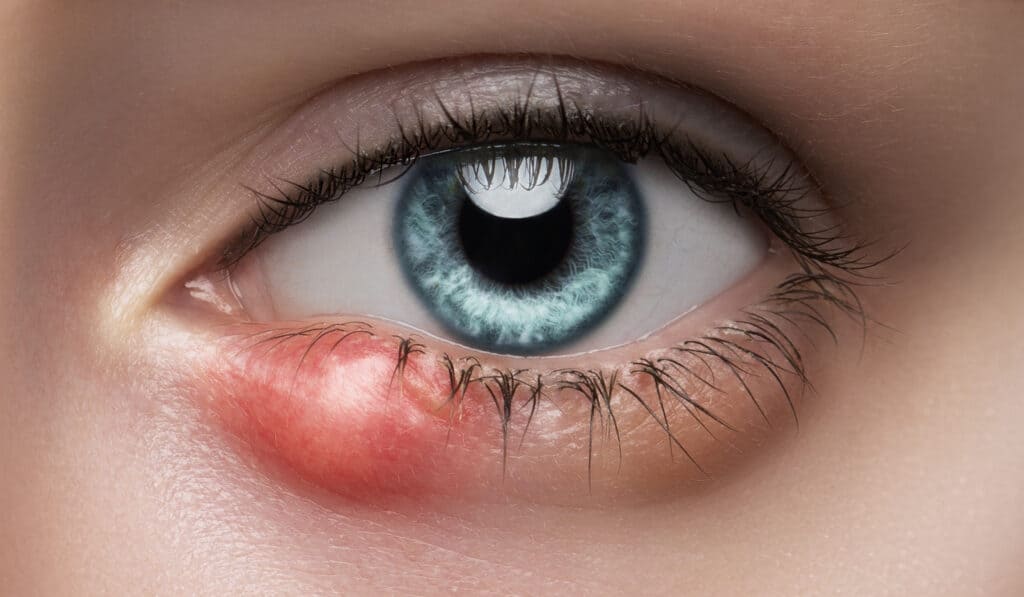
What causes palpebral lesions?
Eyelid or palpebral lesions can be caused by many factors, such as papillomas, chalazion, warts, and cysts.
The most common causes of noncancerous (benign) eyelid lesions are
- Inflammation of a blocked Meibomian gland (called chalazion)
- Infection and inflammation of a gland (called hordeolum)
- Lipid accumulation in the dermis (called xanthelasma)
- Cyst formation of structures in or around the skin (such as epidermal inclusion cyst, cyst of Moll, cyst of Zeiss)
- Melanocyte proliferation in the skin (called nevus)
- Overgrowth of skin cells (called acanthosis)
- Thickening of the skin (called hyperkeratosis) (such as seborrheic keratosis, acrochordon/skin tag)
- Infection of the skin (usually viral, such as verruca vulgaris, molluscum contagiosum)
Other risk factors that may increase your chances of developing these growths include tumours and allergies.
Palpebral Lesions symptoms
If you have an eyelid lesion, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Discomfort in the eye
- Redness or inflammation
- Pain
- Tingling
- A burning sensation
Benign (noncancerous) eyelid lesions may be pigmented or flesh-coloured and often do not cause any pain or discomfort unless you scratch them, which may cause bleeding and pain.
Malignant (cancerous) growths on the eyelid may appear with characteristics such as:
- A smooth, shiny, waxy surface
- A scaly, rough, red, or brown patch
- A red and firm appearance
- A bloody, crusty, or scabbed sore
- A flat, skin-coloured or brown lesion
- A flat, scaly surface that is tender or itchy
If you experience any of the symptoms of palpebral lesions, contact your Vision Pros specialist as soon as possible.

Palpebral Lesions diagnosis
Your ophthalmologist will perform a comprehensive eye exam to diagnose an eyelid or palpebral lesion accurately.
During the exam, your eye doctor will investigate factors such as:
- The duration of the problem
- Changes in the size or appearance of a lesion
- Any history of skin cancer
Your eye specialist will carefully examine the structure of your eyelid for signs of the following:
- Drooping
- Excess tissue
- Retraction problems
- Lesions
- Excessive tearing
- Misdirected eyelashes
In addition to visual observation, your ophthalmologist may recommend other tests such as:
- Biopsy and histopathological analysis
- CT or MRI scans to determine the size and extent of the lesion
- High-resolution ultrasound to analyze buried lesions that are deeper in the eyelid
- Photography to follow growth over time in lesions that are not removed

Palpebral Lesions treatment
If you have an eyelid lesion, it’s important to get an accurate diagnosis to determine the best treatment.
Depending on the type and severity of the palpebral lesion, treatment options may include the following:
- Warm compresses
- Topical or oral antibiotic
- Steroid injections
- Excision
- Curettage
- Electrocautery
- Cryotherapy or cryosurgery
- Laser treatment
Why choose Vision Pros to treat your palpebral lesions?
- Experienced ophthalmology team with expertise in all areas of ophthalmology, optometry, and general eye care.
- Rapid access and referral to world-class comprehensive screening and cutting-edge treatment in a state-of-the-art ophthalmology clinic.
- Holistic, personal, and patient-centric approach to every aspect of eye care.
Book an appointment for your comprehensive eye examination today
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK582155/
- https://www.optometrists.org/general-practice-optometry/guide-to-eye-conditions/dry-eye/eyelid-conditions/lesions-of-the-eyelids/#:~:text=An%20eyelid%20lesion%20is%20a,malignant%20tumors%2C%20and%20structural%20problems.
- https://www.reviewofophthalmology.com/article/eyelid-lesions-diagnosis-and-treatment
- https://www1.racgp.org.au/ajgp/2019/august/eyelid-lesions-in-general-practice
- https://www1.racgp.org.au/getattachment/41c885e4-1d6b-45a2-a578-4bd2276a9cfb/Eyelid-lesions-in-general-practice.aspx
- https://cliniquebellevue.com/en/diseases/palpebral-lesions/#:~:text=Definition,below%20or%20above%20the%20skin.